The network flow problem is to seek the max flow of a network, there are several property of a network.
- Vertex
+ adjacent Edge is those from the vertex out
- Edge
+ link two vertex
+ have a direction
+ have a capacity ( c )
- flow
+ stores how much has been used (f)
+ residual
+ stores the residual room, (= c-f)
Ford-Fulkerson algorithm
see detailed information in blog
https://www.cnblogs.com/luweiseu/archive/2012/07/14/2591573.html
and PPT of professor bdb
http://bioinfo.ict.ac.cn/~dbu/AlgorithmCourses/Lectures/Lec10.pdf
realization
class Edge(object):
def __init__(self, u, v, c):
self.u = u
self.v = v
self.capacity = c
def __repr__(self):
return str(self.u) + "->" + str(self.v) + ":" + str(self.capacity)
class NetworkFlow(object):
def __init__(self):
self.adjacent = {}
self.flow = {}
def addVertex(self, v):
self.adjacent[v] = []
def addEdge(self, u, v, w):
if u == v:
raise ValueError("u == v")
e = Edge(u, v, w)
re = Edge(v, u, 0)
e.redge = re
re.redge = e
self.adjacent[u].append(e)
self.adjacent[v].append(re)
self.flow[e] = 0
self.flow[re] = 0
def getEdge(self, v):
return self.adjacent[v]
def findPath(self, u, v, found):
if u == v:
return found
for e in self.adjacent[u]:
residual = e.capacity - self.flow[e]
if residual > 0 and (e, residual) not in found:
ret = self.findPath(e.v, v, found + [(e, residual)])
if ret != None:
return ret
def maxFlow(self, u, v):
path = self.findPath(u,v,[])
while path != None:
print(path)
flow = min(res for e,res in path)
for e,res in path:
self.flow[e] += flow
self.flow[e.redge] -= flow
path = self.findPath(u,v,[])
return sum(self.flow[e] for e in self.adjacent[u])
example
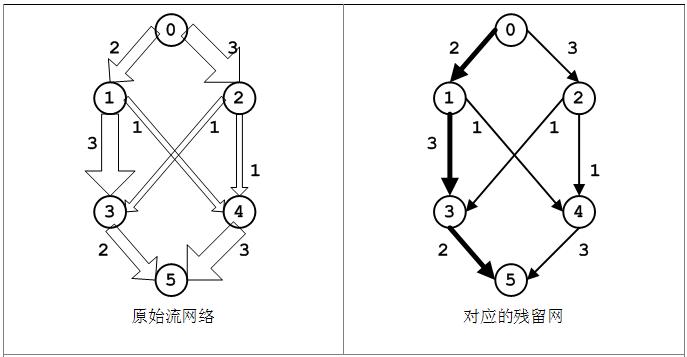
To solve this network, the result is 4.
network = NetworkFlow()
for i in range(6):
network.addVertex(i)
network.addEdge(0, 1, 2)
network.addEdge(0, 2, 3)
network.addEdge(1, 3, 3)
network.addEdge(1, 4, 1)
network.addEdge(2, 3, 1)
network.addEdge(2, 4, 1)
network.addEdge(3, 5, 2)
network.addEdge(4, 5, 3)
The result is correct on this problem, everything seems good since now.
a bad example
The result is correct but takes many steps to solve this problem, and this is mainly because there is a bottleneck on this problem, it is explained clear on the PPT mentioned before.

There are several ways to solve this bad feature

scaling with delta
This method will take only several steps to solve the problem upward.

def findPath(self, u, v, found, delta):
if u == v:
return found
for e in self.adjacent[u]:
residual = e.capacity - self.flow[e]
# compare and make e.capacity > delta
if e.capacity > delta and residual > 0 and (e, residual) not in found:
ret = self.findPath(e.v, v, found + [(e, residual)], delta)
if ret != None:
return ret
def maxFlow(self, u, v):
delta = sum(e.capacity for e in self.adjacent[u]) # set delta
while delta >= 1:
path = self.findPath(u,v,[], delta)
print(delta)
print(path)
while path != None:
flow = min(res for e,res in path)
for e,res in path:
self.flow[e] += flow
self.flow[e.redge] -= flow
path = self.findPath(u,v,[],delta)
delta /= 2 # scale delta
return sum(self.flow[e] for e in self.adjacent[u])
Edmonds-Karp algorithm
use BFS search to find the shortest path

def findShortestPath(self, u, v): # BFS
visited = []
level = [(u,[])]
while level != []:
nextlevel = []
for x,path in level:
visited.append(x)
for e in self.adjacent[x]:
residual = e.capacity - self.flow[e]
if residual > 0 and e.v not in visited:
nextlevel.append((e.v,path+[(e,residual)]))
if e.v == v:
return path+[(e,residual)]
level = nextlevel
Dinic algorithm
use BFS tree to construct a layered network

reference:
http://blog.csdn.net/jwg2732/article/details/78516817
getLayeredNetwork
def getLayeredNetwork(self, u, v):
layered = NetworkFlow()
layered.addVertex(u)
visited = []
level = [u]
count = 1
while v not in level and level != []:
count += 1
visited += level
nextlevel = []
for x in level:
for e in self.adjacent[x]:
residual = e.capacity - self.flow[e]
if residual > 0 and e.v not in visited:
nextlevel.append(e.v)
layered.addVertex(e.v)
layered.addE(e, residual)
level = list(set(nextlevel))
layered.count = count
if v in level:
return layered
maxFlow
def maxFlow(self, u, v):
layered = self.getLayeredNetwork(u, v)
while layered != None:
level = [u]
totalpaths = {}
totalpaths[u] = ([([], sum(e.capacity for e in self.adjacent[u]))])
for i in range(layered.count):
nextlevel = []
nextpaths = {}
for x in totalpaths:
for path, total in totalpaths[x]:
if x in level:
for e in layered.adjacent[x]:
if total == 0:
break
if e.v not in nextpaths:
nextpaths[e.v] = []
nextlevel.append(e.v)
if layered.residual[e] >= total:
nextpaths[e.v].append((path + [e], total))
break
else:
nextpaths[e.v].append(
(path + [e], layered.residual[e]))
total -= layered.residual[e]
level = list(set(nextlevel))
if len(nextpaths) != 0:
totalpaths = nextpaths
for path, total in totalpaths[v]:
for e in path:
self.flow[e] += total
self.flow[e.redge] -= total
layered = self.getLayeredNetwork(u, v)
return sum(self.flow[e] for e in self.adjacent[u])
a executing process example
----------------------------------i= 0
--------------------------x= 0
totalpath {0: [([], 96)]}
level [0]
-------------total: 96 path: []
---------e= 0->1:64 total: 96
---------e= 0->2:32 total: 32
----------------------------------i= 1
--------------------------x= 1
totalpath {1: [([0->1:64], 64)], 2: [([0->2:32], 32)]}
level [1, 2]
-------------total: 64 path: [0->1:64]
---------e= 1->3:64 total: 64
--------------------------x= 2
totalpath {1: [([0->1:64], 64)], 2: [([0->2:32], 32)]}
level [1, 2]
-------------total: 32 path: [0->2:32]
---------e= 2->3:32 total: 32
Push-Relabel algorithm
use a field forward of Edge to judge if the edge is forward or backward.
reference
http://blog.csdn.net/mr_kktian/article/details/53574134

a instance
0.initially

1.s->r1 push, r1->c1,c2,c3 =>t

2.r2->c1 so c1 has a excess=1 need to push back

3.c1->r1->s, push back the excess1 to s

4.s->r1->c1, because only the path to r1 have left capacity, and then c1 push the excess=1 to r2

5.finally

realize
def maxFlow(self, s, t):
self.height[s] = len(self.adjacent)
for e in self.adjacent[s]:
self.flow[e] = e.capacity
self.flow[e.redge] = e.capacity
self.excess[e.v] = e.capacity
self.excess[s] = 0
while True:
exc = [x for x in self.excess if self.excess[x] > 0 and x != t]
judge = False
flags = False
if len(exc) == 0:
break
elif len(exc) == 1 and exc[0] == s:
flags = True
for x in exc:
flag = False
for e in self.adjacent[x]:
if self.height[x] > self.height[e.v]:
if e.forward and e.capacity - self.flow[e] > 0:
bottleneck = min(self.excess[x], e.capacity - self.flow[e])
self.flow[e] += bottleneck
self.flow[e.redge] += bottleneck
self.excess[x] -= bottleneck
self.excess[e.v] += bottleneck
flag = True
elif not e.forward and self.flow[e] > 0:
bottleneck = min(self.excess[x], self.flow[e])
self.flow[e] -= bottleneck
self.flow[e.redge] -= bottleneck
self.excess[x] -= bottleneck
self.excess[e.v] += bottleneck
flag = True
if flag == False:
self.height[x] += 1
judge = True
if judge and flags:
break
return self.excess[t]